Maxine Features
Dashboard UI
- Maxine dashboard UI provides a very interactive way to monitor the configuration, logs, SRD info and the SRD's current status like memory occupied, requests per second etc.
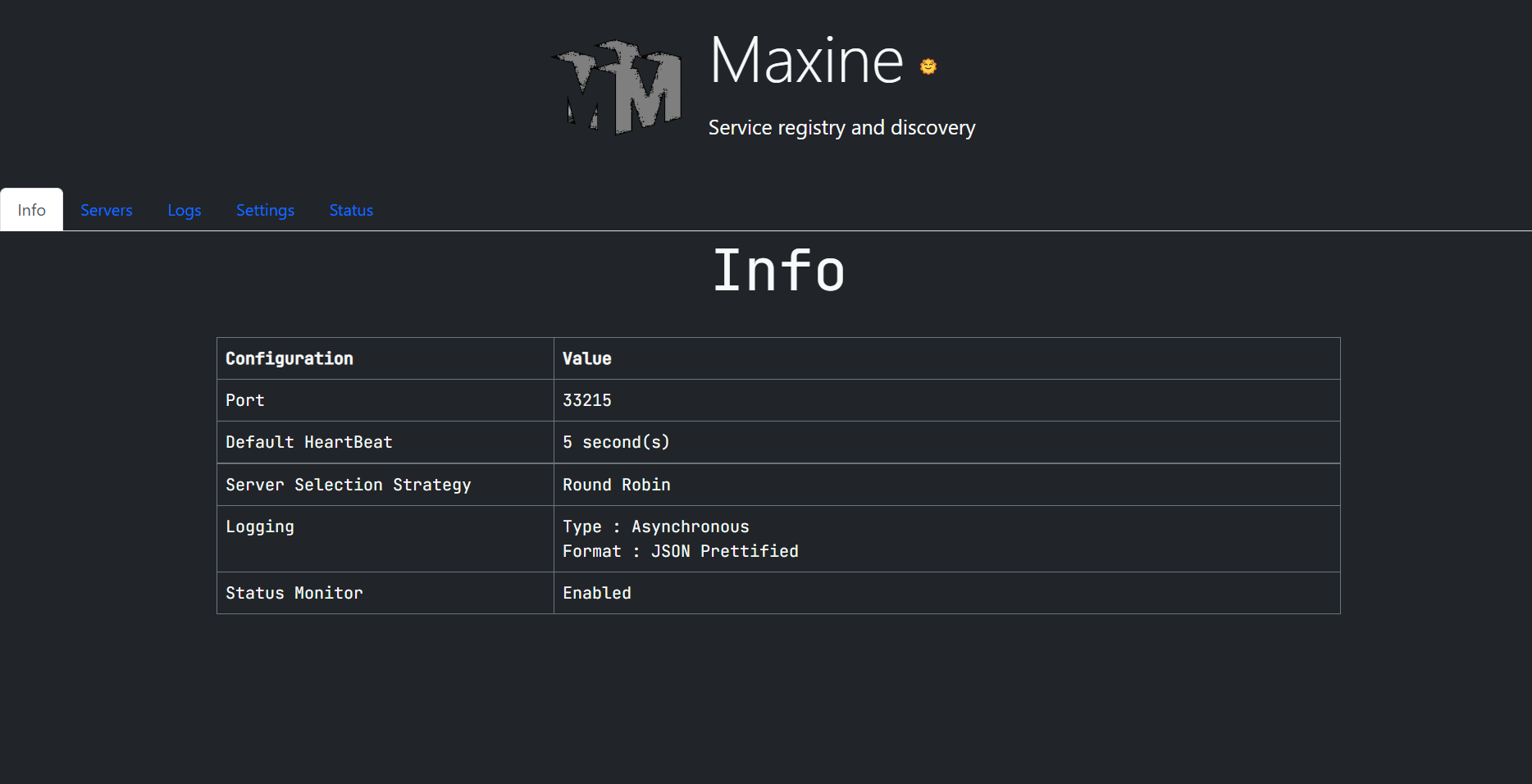
Service registry
- The service registry is the part of Maxine that register or save the service metadata (Extracted data like serviceName, hostName, nodeName, port, SSL, timeOut, weight, path from heartbeat) in memory to make the retrieval faster.
- Also, the SRD replicates the more weighted services (The service that sends a weight of more than one).
- After registering the Service, the SRD will run a thread asynchronously that'll remove that service from the registry once the timeout exceeds and that Service is not re-registered.
- If the service sends the heartbeat before the timeout passes since it was registered, then the thread that was executed earlier will be suspended and a new thread will start doing the same again.
Service discovery
- The service discovery discovers the service that is registered in the registry.
- When the service discovery receives the request, it extracts the serviceName from the request and discovers the service with that service name.
- If discovery finds the single service node with that serviceName, then It'll simply redirect that request to that service's URL.
- If there are multiple nodes of the same service in the registry, then discovery has to distribute the traffic across all of them, that's where Maxine's load balancer comes to rescue.
Load Balancing
- If there are multiple nodes of that service available in the registry, then the discovery needs to distribute the load across those nodes.
- Choosing the right server is a very important thing here because if we're using the server-side and server-specific cache, then choosing the wrong node or server might cost us (High latency especially).
- Here, the Maxine discovery comes with three server-selection strategies.
- Round robin: This strategy is very simple, discovery will start forwarding the request to the next server each server in turn and in order so, it's fairly simple. Note that the requests to the same service name can be redirected to different nodes each time.
- Hashing-based: In this strategy, the discovery hashes the IP of the client and based on that hash, It'll come up with the number and that numbered node will be the chosen server. In Maxine, there are two hashing-based strategies are developed.
HeartBeat
- As we know that in order to let the service registry know that the service is alive, service has to send the heartbeat to the registry and after certain period of time (timeout), that service will be removed from the registry automatically so becore that service gets deregistered from registry, the service has to send the heartbeat again, That's why we call it a heart beat because it literally keeps beating in a period of time, Let's understand what is this heartbeat.
- Heartbeat in maxine is a special kind of request that contains all the meta data about the service.
- Basically, the once the service is alive, It'll start sending this request to the registry and this request will have some parameters (JSONised ofcourse) that represents the service metadata.
- Below is the list and explaination of all the parameters that needs to be passed with the heartbeat request. (All the necessary parameters are marked with Astrik (*))
- ServiceName (*): The name of the service, Note that the service name will be same for multiple nodes of the same service so that maxine can identify the nodes and distribute the traffic evenly.
- hostName (*): This represents the hostname (IP Address typically) of the service. This is optional parameter. Maxine can extract the host address out of request so if this parameter is not passed, It'll be extracted from the request. However, it is always prefferable to pass the hostname manually because jf the service is masked by some proxy and if the firewall rules are strict and complicated, then the discovery will redirect to the url that might not work because of security issues.
- nodeName (*): If the service is replicated and has multiple nodes, then the serviceName in all the nodes will be the same but the nodeName will be different. Multiple nodes with the same service name will be registered to Maxine and then discovery server will balance the load evenly.
- port (Default 80 or 443): The port number that the service is running on top of.
- ssl (Default false): To determine if ssl is configured on the host where service is running or not. If ssl is true, then the service URL will be have HTTPS (443) otherwise HTTP (80) will be used.
- timeOut (Default 5): Defines the amount of time (typically in seconds only) after which service should be deregistered. Once the service is registered, It'll be deregistered after the timeout provided in the heartBeat. Once the service sends the heartBeat again in the given timeout then the tineout will be reset.
- weight (Default 1): If the service is replicated with multiple nodes and if any of those nodes is deployed on more powerful machine and configuration, it is acceptable that that particular node has more computational power and ability to serve more number of request in the less or the same amount of time. So, weight property will replicate that node into registry that many times. Note that the limit of weight property is 10, meaning that a node can be 10x more powerful than the rest of the nodes.
- path: URL path like /api/v1 or somethings, defines the default path after IP where discovery will redirect the request to.
Example:
Heartbeat Request
{ "serviceName": "bed-mgmt", "hostName" : "10.72.131.21", "nodeName" : "Node-4", "port": 8080, "ssl" : true, "timeOut" : 30, "weight" : 5, "path" : "/api/v3" }Response (Service registered)
{ "hostName": "10.72.131.21", "nodeName": "Node-4", "serviceName": "bed-mgmt", "timeOut": 30, "weight": 5, "address": "https://10.72.131.21:8080/api/v3", "registeredAt": "9/19/2022, 2:09:34 PM" } - Maxine client takes care of sending the heartbeat to the registry but before you start the server, you have to provide all these parameters in the properties or configurations.
- If you pass the above example request to Maxine registry and then open the Maxine UI's servers page, it'll show the registered server like given below.
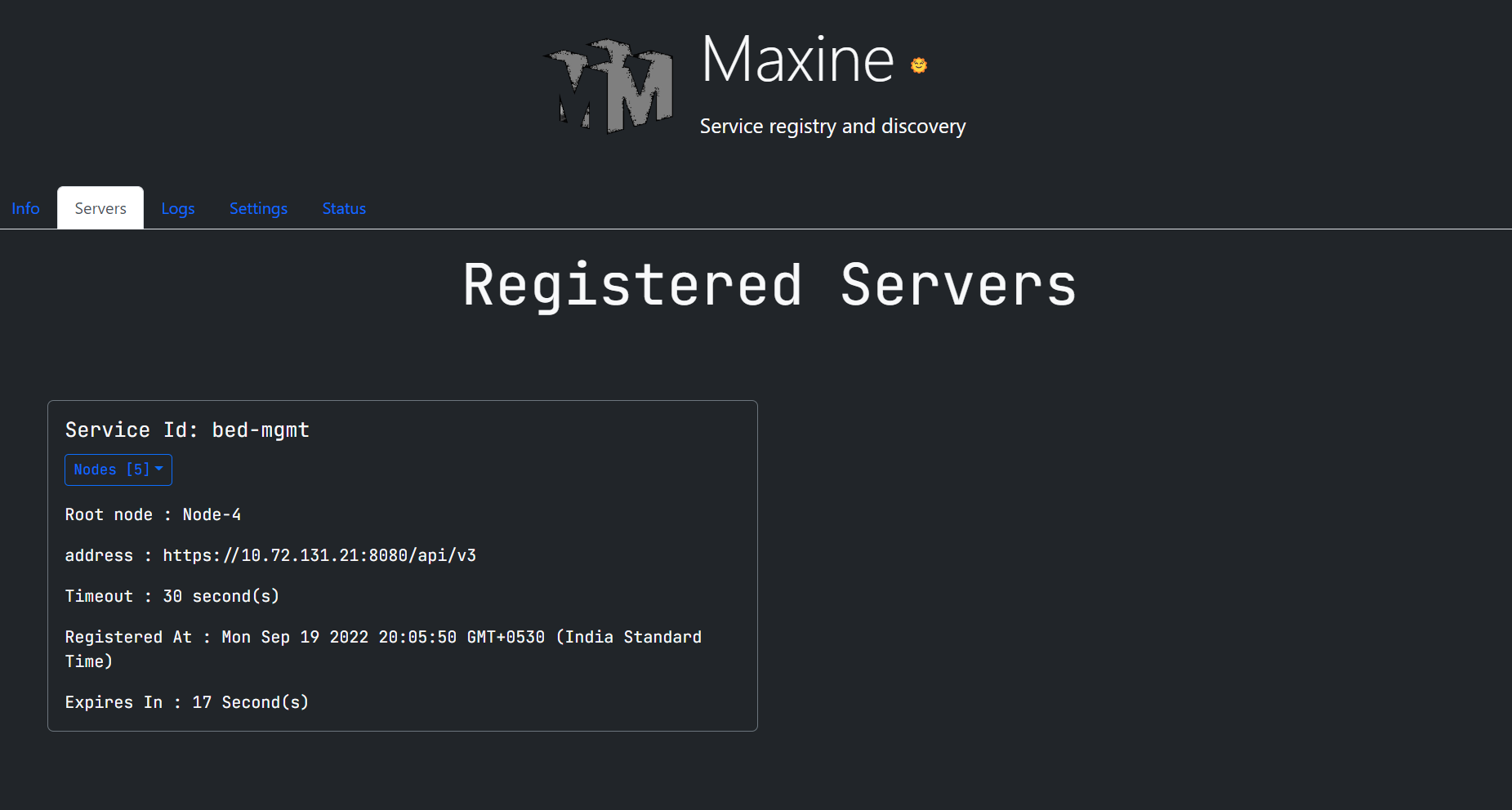
Asynchronous logging
- For Maxine SRD, logging is by default enabled and once you start the server, It'll start showing console logs, apart from that it'll also start storing logs into the files.
- But, the log files get created with some limits, The maxine has predefined value of maximum size of one log file, after that, It'll start to write the logs in the new file.
- In the logging part, all these files will get named properly and they're always available in the logs directory but, in the production environment, most probably the OS will be based on CLI and interacting with logs from there is not that easy.
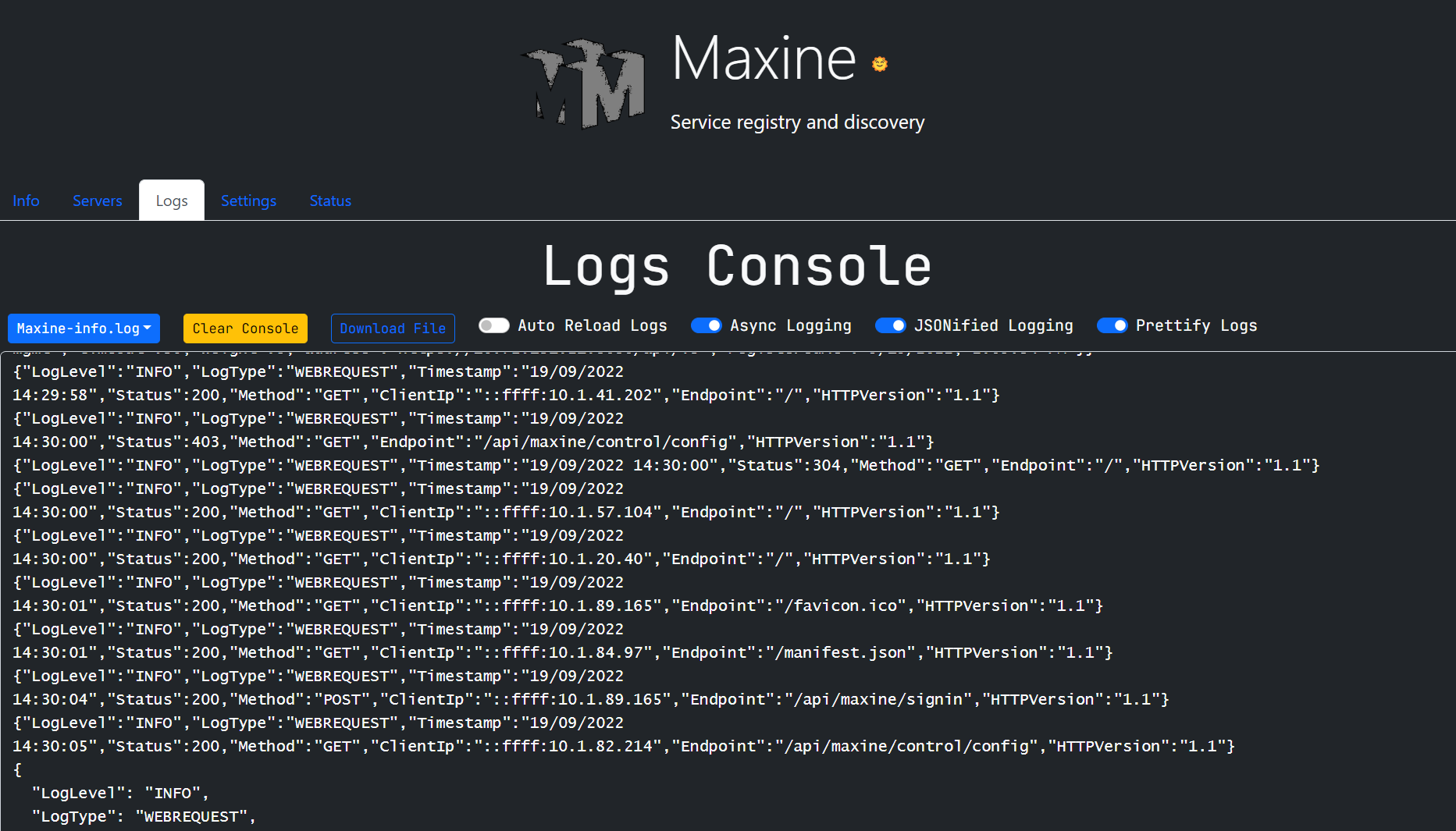
- So, to interacting with logs easily and directly, Maxine UI has Logging tab in it.
- From logging UI, you can control pretty much everything related to logging, you can turn on and off the asynchronous logging, you can JSONify the logs, Prettified JSONify the logs. Also, you can turn off the JSONified logs to make maxine log everything in plain format.
- Apart from that, in this Logging UI, there is also a logging console that'll show all the maxine logs live.
- Also, the old and archived logs will be available on UI, you can download the old and archived logs from the dropdown given right above the Logging console.
- Also, if you notice in the given picture, maxine supports the asyncronous logging, you can turn off and on it from the logging panel of the UI. It's recommended to keep the async logging on because it can significantly reduce the latency to serve requests.
Config control
- Maxine config control provides interactive way to manage the configuration.
- the Settings and Logging tab provides options to monitor and manipulate the Maxine configuration.
- There are given configurations that can be modified in order to change the SRD's behaviour
- Auto Reload Logs : To automatically reload logs in the UI
- Async Logging : To turn on and off the Async logging
- JSONified Logging : To Jsonify the logs, Logs console will show plain logs if turned off.
- Prettify Logs : To pretify the JSONified logs (Works only if JSOnified logging is turned on).
- Default heartbeat : To modify the default heartbeat timeout if the heartbeat is not bringing the timeout parameter from service.
- Server selection strategy : To change the load balancer's server selection strategy. By default, it's Round robin but can be changed to consistent hashing or randezvouz hashing.
- Status monitor : To turn on and off the status monitor.